Diabetes Defined
 Diabetes is a disease wherein the body is unable to use energy from food because of a breakdown in digestion. Basically, it occurs when the pancreas does not produce insulin, or in some cases the pancreas does produce insulin but the individual’s body resists it. A lack of insulin means that the sugar in food is unable to be converted to energy. This results in high levels of sugar in the blood stream. When the body does not have enough insulin in relation to the amount of sugar in their bloodstream, or they have trouble creating insulin, the glucose will remain in the blood at elevated levels.
Diabetes is a disease wherein the body is unable to use energy from food because of a breakdown in digestion. Basically, it occurs when the pancreas does not produce insulin, or in some cases the pancreas does produce insulin but the individual’s body resists it. A lack of insulin means that the sugar in food is unable to be converted to energy. This results in high levels of sugar in the blood stream. When the body does not have enough insulin in relation to the amount of sugar in their bloodstream, or they have trouble creating insulin, the glucose will remain in the blood at elevated levels.
In some cases monitoring one’s diet can prevent pre-diabetes symptoms and therefore decrease the chances of contracting the disease. But if someone is genetically predisposed to the disease or has had a poor diet for most of their life, they will have a higher chance of developing diabetes. Medically, it is referred to as Diabetes Mellitus, but practically, the disease is broken down into two main types; type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Difference between Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
 Type 1 diabetes is common in children and individuals under the age of 20. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas produces little to no insulin, due to pancreas cells being destroyed. Because of this permanent destruction of the cells, individuals with Type 1 diabetes will have the disease for life and will need to use insulin shots or an insulin pump for daily treatment. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their diets as well as incorporate exercise into their weekly routines to prevent their blood sugar from fluctuating beyond normal limits.
Type 1 diabetes is common in children and individuals under the age of 20. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas produces little to no insulin, due to pancreas cells being destroyed. Because of this permanent destruction of the cells, individuals with Type 1 diabetes will have the disease for life and will need to use insulin shots or an insulin pump for daily treatment. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their diets as well as incorporate exercise into their weekly routines to prevent their blood sugar from fluctuating beyond normal limits.
Type 2 diabetes is more commonly found in individuals who become overweight throughout their lifetime, although more children and young adults are being diagnosed, who are not incorporating enough activity into their weekly schedules. Type 2 diabetes is when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the individual’s body does not use the insulin in the right away.
How Diabetes is diagnosed
When a physician believes their patient has Type 1 diabetes they will take a blood, urine, and insulin test giving a complete diagnosis in a short period of time. Though some call type 1, ‘juvenile diabetes,’ it can actually occur at any age.
Symptoms
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes may have symptoms like fatigue, increased hunger, excessive thirst, and they may experience frequent urination. Other symptoms may include nausea, weight loss, and stomach pain.
 Diabetes Cure
Diabetes Cure
There is no cure for diabetes, and Type 1 is a life-long condition. There are many ways for individuals to control their blood sugar levels and keep them in a safe range daily. Regardless of age all individuals with Type 1 diabetes will need to monitor their diet, exercise, and insulin everyday. To test blood glucose and blood sugar throughout the day individuals may use a device that tests a drop of their blood, this way they can determine if they need more insulin.
Diet
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes are able to eat all the same foods as individuals without diabetes but they must monitor their intake. All carbohydrates must be tracked, and individuals should try to have a well-balanced healthy diet on a daily basis. Your doctor can help you determine what your diet should consist of. They will most probably refer you to a nutritionist upon your diagnosis.
 Diabetes Life Expectancy
Diabetes Life Expectancy
Life expectancy varies between men and women with type 1 diabetes, depending on how balanced their diets are, how much exercise they incorporate into their weekly routines, and how well they monitor their blood sugar levels. In general, men can lose about eleven years while women’s lives are cut short by about thirteen years when they live with type 1 diabetes. The high blood sugar overtime can cause kidney disease, heart disease, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure. High blood pressure and high cholesterol both contribute to poor circulation which can damage the individual’s eyes, heart, kidneys, and nerves which all contribute to a shorter life expectancy.
 Diabetes Treatment
Diabetes Treatment
Some common treatments for individuals with type 1 diabetes include the following:
- Taking insulin
- Carbohydrate counting
- Blood sugar monitoring
- Eating healthy foods
- Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight
Diabetes in Children
 Most parents are very scared and upset when they hear that their child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, but today there are many ways to cope with the disease and make sure your child is healthy and strong. About 13,000 children are diagnosed with the disease every year. The disease will not prevent your child from doing what all other children do, the main change is constantly checking your child’s blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you plenty of information that will seem overwhelming at first, but with time it will become part of your lifestyle and be very manageable.
Most parents are very scared and upset when they hear that their child is diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, but today there are many ways to cope with the disease and make sure your child is healthy and strong. About 13,000 children are diagnosed with the disease every year. The disease will not prevent your child from doing what all other children do, the main change is constantly checking your child’s blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you plenty of information that will seem overwhelming at first, but with time it will become part of your lifestyle and be very manageable.
Diabetes Causes
The cause of Type 1 diabetes is unknown, but scientists have discovered that the immune system in individuals with type 1 diabetes, destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas instead of fighting off harmful bacteria and viruses. Genetics may also be a factor in contracting the disease as well as exposure to certain viruses.
Diabetes Autoimmune
Diabetes autoimmune refers to a process in the body where it mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing cells, or beta cells. It occurs in genetically predisposed individual’s and can be a cause of type 1 diabetes. The cause of autoimmune destruction is unknown, but environmental factors could have a part to play in its contraction.
Diabetes and Pregnancy
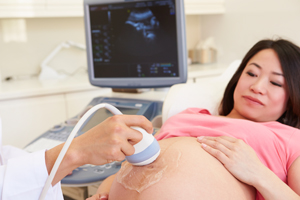 Women with type 1 diabetes can get pregnant and have healthy babies but they will generally have a lot more to think about than women who do not have the disease. They will visit the doctor a lot more and will be followed closely by their obstetrician, and nutritionist. Pregnant women with diabetes often get extra ultra sounds, bio-physicals, and non stress tests. Some women use a glucose monitor and prick their finger up to ten times a day to manage their insulin levels. It may seem like a lot throughout the 9 months of pregnancy but all of the precautions are to make sure their babies are healthy at delivery.
Women with type 1 diabetes can get pregnant and have healthy babies but they will generally have a lot more to think about than women who do not have the disease. They will visit the doctor a lot more and will be followed closely by their obstetrician, and nutritionist. Pregnant women with diabetes often get extra ultra sounds, bio-physicals, and non stress tests. Some women use a glucose monitor and prick their finger up to ten times a day to manage their insulin levels. It may seem like a lot throughout the 9 months of pregnancy but all of the precautions are to make sure their babies are healthy at delivery.
Diabetes Facts
Even though most people know someone who has type one diabetes, there are some facts that might come to some as a surprise. Below are a list of commonly known facts about diabetes:
 1/3 of people with diabetes do not know they have the disease
1/3 of people with diabetes do not know they have the disease- About 5% of people with diabetes have type 1 diabetes
- A meal plan for a person with diabetes isn’t very different to one recommended for people without diabetes
- Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in working age adults
- Individuals with diabetes are twice as likely to develop heart disease
- Diabetes costs $174 billion annually
- 29.1 million Americans had diabetes in 2012
- About 1.25 million American children are living with Type 1 diabetes
- Diabetes was the 7th leading cause of death in the US in 2010
Diabetes Ribbon
The diabetes awareness ribbon is a short piece of colored ribbon that is folded into a loop, the ribbon is a statement which provides support for the cause surrounding the disease. The diabetes ribbon is gray and blue with a red dot.
Diabetes Awareness
Today there is a large community that supports individuals with diabetes, and educates others who do not have the disease. November 14th is World Diabetes Day and the whole month is dedicated to national diabetes awareness. National diabetes month was established in 1975, and today there are many associations that raise awareness for the disease as well as for programs working to educate, advocate, and cure Type 1 diabetes.
Listed below are a few of these associations:
- American Diabetes Association
- Beyond Type 1
- Diabetes Hands Foundation
- Diabetes Community Advocacy Foundation
- International Diabetes Federation
- Project Blue November
- T1 International
Diabetes and Alcohol
As a diabetic it is crucial to take caution while drinking, and not to drink on any empty stomach. It is important to drink slowly and to keep a zero caloric beverage close by to keep yourself hydrated such as water, iced tea, or diet soda.
Can Type 1 Diabetes be Reversed?
Type 1 Diabetes symptoms can be reduced with a healthy diet and exercise, but as of now the disease cannot be reversed.

Type 1 Diabetes and Depression
Depression in individuals with Type 1 diabetes is not more common than individuals without the disease, but people with Type 1 diabetes have a greater risk of depression than those without. The stress of having the disease, the feeling of separation from friends and family, and anxiety can all create the feeling of depression in someone with Type 1 diabetes.