Diabetes is a common word. Although we hear it sometimes on a daily basis and probably know of friends or family with the disease, there are many facts and assumptions made about the disease that are not necessarily true. Studying more about diabetes can help individuals understand it better. The condition is commonly called Diabetes Mellitus, (Mellitus is just the fancy word for type one and type two diabetes). Below are some facts about the disease and its effect on patients who have it.
Diabetes Defined
 Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to use energy from food because it is not digesting it properly. This occurs mainly because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or in some cases the pancreas does produce insulin but the individuals body resists it.
Diabetes occurs when the body is unable to use energy from food because it is not digesting it properly. This occurs mainly because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or in some cases the pancreas does produce insulin but the individuals body resists it.
The underlying problem caused is that the individual ends up with too much blood sugar in their body compared to the amount of insulin their pancreas is providing. When the body does not have enough insulin in relation to the amount of sugar in their bloodstream, or they have trouble creating insulin, the glucose will remain in the blood and elevate the individual’s sugar levels.
Type One
 Type one diabetes is common in individuals under the age of 20 and in children. Type one diabetes is when the pancreas produces little to no insulin. This is primarily due to pancreas cells being destroyed. Individuals with Type one diabetes will have the disease for life and will need to use insulin shots or an insulin pump for treatment.
Type one diabetes is common in individuals under the age of 20 and in children. Type one diabetes is when the pancreas produces little to no insulin. This is primarily due to pancreas cells being destroyed. Individuals with Type one diabetes will have the disease for life and will need to use insulin shots or an insulin pump for treatment.
Individuals with Type one diabetes need to monitor their diet as well as incorporate exercise into their weekly routine to prevent their blood sugar from fluctuating beyond healthy limits.
Type Two
Type two diabetes is more commonly found in individuals who become overweight throughout their lifetime, although more children and young adults are being diagnosed with this condition of late, as they are not incorporating enough activity into their weekly schedules.
Type two occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or the individual’s body does not use the insulin in the right away.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is seen in about 4% of women who are in their second trimester of pregnancy. Luckily this type of diabetes will go away once the baby is born. The older the woman is the more likely she is to develop gestational diabetes. It also puts her at a higher risk of contracting Type two diabetes later in life.
Diabetes Insipidus
This is a condition that makes an individual very thirsty, and as a result makes them pee a lot. It is caused when a person’s brain makes something called an antidiuretic hormone (ADH). This hormone tells their kidneys to hold onto water, making their urine more concentrated. When the body does not make enough ADH the kidneys cannot retain water even if the individual is dehydrated.
Symptoms
 Symptoms vary for different types of diabetes but symptoms for diabetes insipidus can include:
Symptoms vary for different types of diabetes but symptoms for diabetes insipidus can include:
- excessive thirst
- frequent urination
- Dehydration
- Unexplained weakness
- Irritability
- Muscle Pains
Treatment
Doctors will tell their patients to constantly get enough fluids to replace the loss of water they intake. Individuals with central diabetes insipidus can take medications such as desmopressin, which comes in a nasal spray; this replaces their missing ADH. Although diabetes insipidus does not cause kidney failure or dialysis it can cause extreme dehydration, which is why individuals should always have a drink nearby if they know they will be exercising or in hot weather.
Facts about diabetes
 Currently there are over 260 million people worldwide with diabetes
Currently there are over 260 million people worldwide with diabetes- 65,000 new cases of diabetes are diagnosed each year
- 80 years after the discovery of insulin, there are still many people around the world who either cannot access insulin on a regular basis or at all
- Diabetes can damage organs including tissue of kidneys, eyes, peripheral nerves, vascular tree, eyes (causing blindness) and be the cause of loss of limbs in the lower extremities due to poor circulation
- Type 2 diabetes is preventable in approximately 80% of all cases
- More than half of all people who are diabetic don’t know they have diabetes
How Diabetes is diagnosed
When a physician believes their patient has Type one diabetes they will take a blood, urine, and insulin test giving a complete diagnosis in a short period of time. Contrary to its common name, ‘juvenile diabetes,’ the condition can actually occur at any age.
Symptoms
Individuals with Type one diabetes may have symptoms of fatigue, increased hunger, excessive thirst, and may experience frequent urination. Other symptoms may include nausea, weight loss, and stomach pain.
Diabetes Test
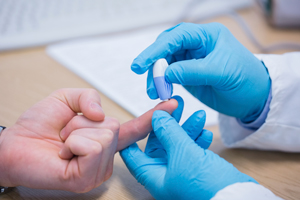 One diabetes test is called the RPG, which stands for a Random Plasma Glucose test. The individual does not need to fast for the test, and it consists of a simple blood test. The individual’s blood is sent to be analyzed. A blood glucose reading without fasting is considered normal if it reads under 200 mg/dl. When the results are over 200 mg/dl and the individuals possesses strong symptoms such as being very thirsty or frequent urination diabetes is quite likely. The results of one test will not permit a doctor to diagnose an individual with diabetes; they will likely take various tests and compare one another before diagnosing an individual.
One diabetes test is called the RPG, which stands for a Random Plasma Glucose test. The individual does not need to fast for the test, and it consists of a simple blood test. The individual’s blood is sent to be analyzed. A blood glucose reading without fasting is considered normal if it reads under 200 mg/dl. When the results are over 200 mg/dl and the individuals possesses strong symptoms such as being very thirsty or frequent urination diabetes is quite likely. The results of one test will not permit a doctor to diagnose an individual with diabetes; they will likely take various tests and compare one another before diagnosing an individual.
Diabetes Cure
To date, there is no cure for diabetes, and Type one is a life-long condition. There are many ways for individuals to control their blood sugar levels and keep them in a safe range. Regardless of age, all individuals with Type one diabetes will need to monitor their diet, exercise, and insulin levels daily. To test blood glucose and blood sugar throughout the day individuals may use a device that tests a drop of their blood. With this they can determine if they need more insulin.
Individuals with Type two diabetes can manage their diabetes with healthy eating and exercise. If they are unable too, their doctor may prescribe them insulin or oral medications (pills) to help meet their blood glucose levels.
 Diabetes socks
Diabetes socks
In about 10% of individuals with diabetes, foot ulcers will occur. Diabetic socks are used to control the moisture in the foot to reduce fungal infection or create a cushion to prevent future foot ulcers.
Individuals with type one diabetes are able to eat all the same food as individuals without diabetes but they must monitor their intake. All carbohydrates must be tracked, and individuals should try to have a well-balanced healthy diet on a daily basis.
Diabetes in Women
Diabetes can be hard to monitor for both men and women, as it becomes a part of ones lifestyle. Diabetes in women can be even more difficult and carry a burden on them as it can affect their unborn children. Diabetes can cause birth defects in babies as well as miscarriages. In some cases, women with diabetes are more likely to have heart attacks at a younger age than women without diabetes. Some women can experience less interest in sex due to depression from contracting diabetes and eating disorders are also more common in women who have the condition




